HTTP Proxy for accessing internal API – quick setup
Setting up an HTTP proxy can often be useful to reach internal network servers from a different device or machine that does not have direct access to said network. A common case is accessing an internal backend API from a mobile device that shares the same Wi-Fi as the PC that is connected to the VPN. Here are a few simple steps to set up an HTTP proxy.
- Install the Squid Proxy (an HTTP Proxy) relevant for your system.
- Configure the proxy using the squid.conf file in the installation directory (or use the tray icon):
- Your local network configuration should be present in the config file by default, e.g.:
acl localnet src 192.168.0.0/16 # RFC1918 possible internal network
# (...)
# Example rule allowing access from your local networks.
# Adapt localnet in the ACL section to list your (internal) IP networks
# from where browsing should be allowed
http_access allow localnet
# Squid normally listens to port 3128
http_port 3128
- Add your internal DNS servers to the list to resolve internal domain names (optional):
dns_nameservers 8.8.8.8 208.67.222.222 <insert_your_dns_server_ip>
To discover a DNS server of an internal network, run ipconfig /all on Windows and cat /etc/resolv.conf on Linux.
- Add your custom hosts to resolve custom domain names (optional):
# For Windows 10: hosts_file C:/Windows/System32/drivers/etc/hosts
# For Linux: hosts_file /etc/hosts
hosts_file C:/Windows/System32/drivers/etc/hosts
Restart the Squid Proxy using the tray icon or command line (/etc/init.d/squid restart or service squid<TAB> restart on Linux).
3. Make sure the Squid Proxy server is accessible on your local network. Come back to this step if the proxy does not work after step 4, i.e. is not reachable from the client using telnet <IP> <PORT>. You might need to expose the port in your firewall. For example, on Windows this can be done in Control Panel > System and Security > Windows Firewall > Advanced Settings > Inbound Rules > New Rule.
4. Configure the client to use the HTTP proxy:
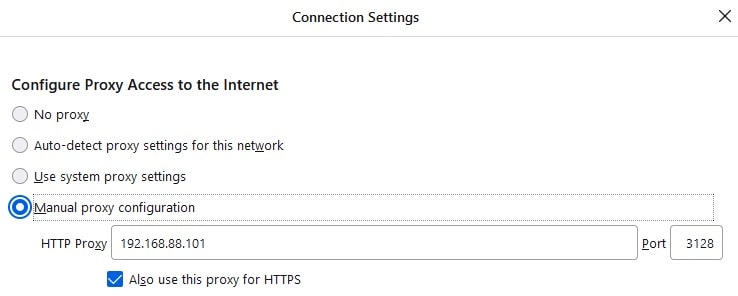
- Firefox: Settings > Network Settings > Connection Settings or search for 'Proxy';
- Chrome: Settings > Advanced > System > Change proxy settings or command-line
google-chrome --proxy-server="http://proxy-ip:proxy-port"; - Android/iOS: Settings > Wi-Fi > Tap (iOS) or Long (Android) press your WiFi network name > Modify network (Android) > Proxy Server > Manual;
- Windows: Settings > Network & Internet > Proxy > Manual proxy setup;
- Ubuntu: System Settings > Network > Network Proxy > Manual.
For the IP address of the proxy server, use the local address of the machine you're running the proxy on. Usually, it will be something like 192.168.x.x (IpV4 Address from running ipconfig on Windows and hostname -I on Linux). As for the port, it is 3128 by default.
Ideally, after these four steps, you should be able to connect to your internal API using internal IP as well as internal domain names.
