BottomAppBar onHide listener
BottomAppBar from the com.google.android.material: material library is a very handy component that allows you to attach an additional bar at the bottom of the screen in Android. This is a great option from the UX perspective, as it is much easier for the user to reach the button at the bottom than with the standard menu at the top.
A very interesting property of the BottomAppBar component is hideOnScroll. Setting its value to true causes the bar to hide or appear when scrolling down or up. This behavior allows you to slightly increase the area displayed by the container. Of course, provided that the user doesn't need to access the buttons on the bottom bar at all times.
Basic configuration
An exemplary configuration of a layout with BottomAppBar looks as follows (you will probably need to adjust it to your needs):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.coordinatorlayout.widget.CoordinatorLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/products_recycler_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
app:layoutManager="androidx.recyclerview.widget.LinearLayoutManager" />
<com.google.android.material.bottomappbar.BottomAppBar
android:id="@+id/bottom_app_bar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
app:contentInsetStart="0dp"
app:fabAlignmentMode="center"
app:fabCradleMargin="8dp"
app:fabCradleRoundedCornerRadius="32dp"
app:hideOnScroll="true">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/sort_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="?android:selectableItemBackground"
android:contentDescription="@string/sort"
android:enabled="false"
android:src="@drawable/ic_sort" />
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/add_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="?android:selectableItemBackground"
android:contentDescription="@string/add_manual"
android:enabled="false"
android:src="@drawable/ic_add_manual" />
<View
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="2" />
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/search_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="?android:selectableItemBackground"
android:contentDescription="@string/search"
android:enabled="false"
android:src="@drawable/ic_search" />
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/help_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="?android:selectableItemBackground"
android:contentDescription="@string/switch_view"
android:enabled="false"
android:src="@drawable/ic_help_outline" />
</LinearLayout>
</com.google.android.material.bottomappbar.BottomAppBar>
<com.google.android.material.floatingactionbutton.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/scan_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:contentDescription="@string/scan"
android:enabled="false"
android:src="@drawable/ic_add_on_secondary"
app:fabSize="normal"
app:layout_anchor="@+id/bottom_app_bar" />
</androidx.coordinatorlayout.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
The parent container here is CoordinatorLayout, inside it we have a sample list based on RecyclerView, which we can scroll through. Then the BottomAppBar with four buttons and finally the FAB button embedded in the center of the bottom bar.
Implementation of an onHide listener
Sometimes we may need a way to bind to the visibility status change of the bottom bar. For example, such a listener will be useful in the event that we want to change the icon and behavior of the FAB button.
The CoordinatorLayout.Behavior class, or actually its subclass com.google.android.material.bottomappbar.BottomAppBar.Behavior, is responsible for hiding and displaying the bottom bar. The general class hierarchy looks like this:

Without going much into details, the two methods we are interested in are:
- HideBottomViewOnScrollBehavior#slideUp();
- HideBottomViewOnScrollBehavior#slideDown().
In there you will find the logic for hiding and showing the bar. What's more, we are able to override these methods without much problem. Similarly to the base class, we will add a state to our listener so that it is only called when the bottom bar shows up or starts disappearing:
import com.google.android.material.bottomappbar.BottomAppBar
abstract class HideListenableBottomAppBarBehavior : BottomAppBar.Behavior() {
private enum class State {
SCROLLED_DOWN, SCROLLED_UP
}
private var currentState: State? = null
abstract fun onSlideDown()
abstract fun onSlideUp()
override fun slideDown(child: BottomAppBar) {
super.slideDown(child)
if (currentState == State.SCROLLED_DOWN) return
currentState = State.SCROLLED_DOWN
onSlideDown()
}
override fun slideUp(child: BottomAppBar) {
super.slideUp(child)
if (currentState == State.SCROLLED_UP) return
currentState = State.SCROLLED_UP
onSlideUp()
}
}
Now, all we have to do is apply our new listener to the layout.
In general, BottomAppBar implements the AttachedBehavior interface and thus the getBehavior(). By default, it's initialized with the standard behavior. Hints for how to overwrite it can be found in the javadocs of the mentioned interface. This can be done through the LayoutParams#setBehavior() method.
After initializing the view (in a fragment or activity), we change the behavior of the bottom bar (here I use kotlinx synthetic to get the reference to the view):
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState)
val params = bottom_app_bar.layoutParams as CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams
params.behavior = object : HideListenableBottomAppBarBehavior() {
override fun onSlideDown() {
scan_button.setImageDrawable(ContextCompat.getDrawable(context, R.drawable.ic_top))
}
override fun onSlideUp() {
scan_button.setImageDrawable(ContextCompat.getDrawable(context, R.drawable.ic_add))
}
}
}
}
As a result, the icon of the FAB button changes:
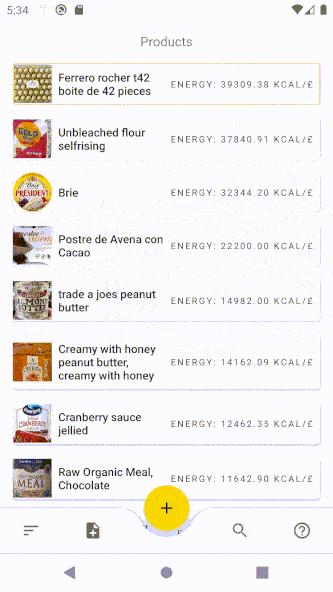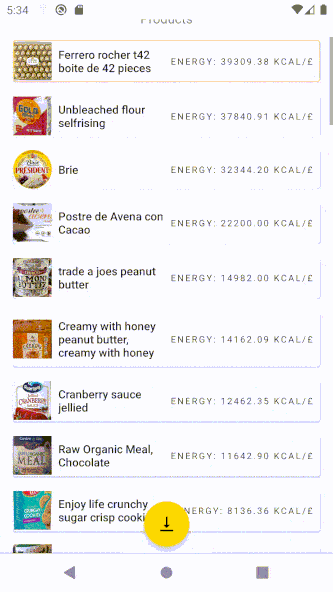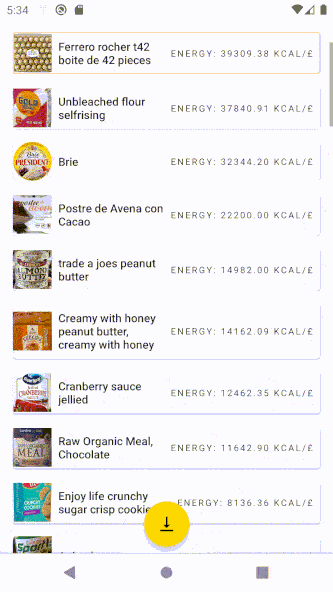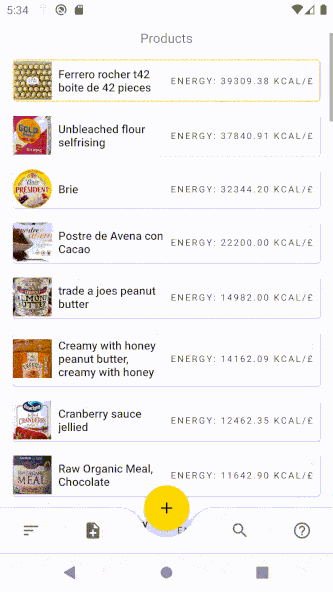
Final tips
If you want to have more control over the state of the layout, you can then take a look at onNestedScroll method of the com.google.android.material.behavior.HideBottomViewOnScrollBehavior class. Overwriting it will allow you to get a reference not only to the bottom bar but also to the container you are scrolling. The parameters will provide more information on the direction of the scrolling. This way, you will be able to define additional events depending on how far the contents of the container have been scrolled.
