Libraries included with IntelliJ database data extractors
The database data extraction in IntelliJ is a very extensible feature that allows user to copy selected columns and rows of the database query result. The fundamental interface described in the documentation describes how to define your own extractor using Groovy or JavaScript.
IntelliJ delivers an API in the form of variables with some specific methods for accessing tables and columns. Through its use, you can construct your own extraction result. However, this tool provides much more besides what is documented.
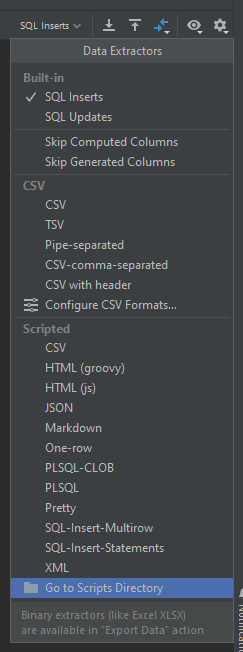
Getting to the bottom of the case – DbSqlUtil
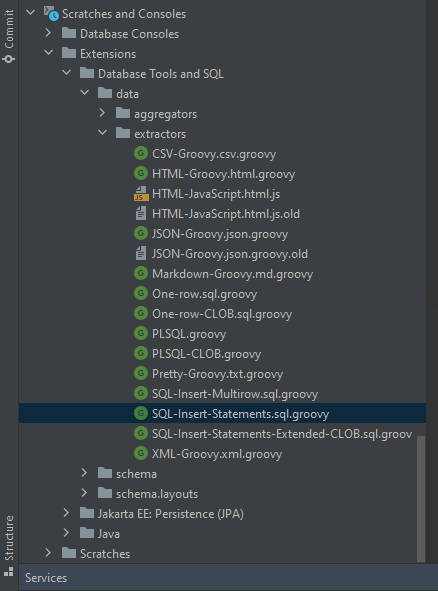
Looking at the extractors provided by IntelliJ, you will find a reference to the com.intellij.database.util.DbSqlUtil class.
If you want to find out how the frequently used areKeywordsLowerCase method works, you will quickly notice
that you cannot view its implementation (CTRL + Shift + A > Go to implementation).
The problem turns out to be more general as the IDE doesn't detect any errors until runtime.
Given that Groovy follows the same class loading model as Java, you can try to get information about the classes used. All you need to do is print information about the hierarchy of ClassLoaders that loaded the Groovy script. Let's create a debug data extractor that lists the classpath together with the class loaders:
def printClassPath(classLoader, depth) {
OUT.append("${depth}. ${classLoader.class.name}: ")
.append(String.valueOf(classLoader)
.replace(",", ",${System.lineSeparator()}")
.replace("(", "${System.lineSeparator()}(${System.lineSeparator()} ")
.replace(")", "${System.lineSeparator()})")
)
.append(System.lineSeparator())
if (classLoader instanceof URLClassLoader) {
classLoader.getURLs().each { url ->
OUT.append("- ")
.append(String.valueOf(url))
.append(System.lineSeparator())
}
}
if (classLoader.parent) {
printClassPath(classLoader.parent, depth + 1)
}
}
OUT.append("Classpath: ${System.getProperty("java.class.path")}${System.lineSeparator()}")
OUT.append("Top-down ClassLoader hierarchy:${System.lineSeparator()}")
printClassPath(this.class.classLoader, 1)
In IntelliJ 2023.2.2, I got the following output when trying to extract any query result data:
Classpath: ...
Top-down ClassLoader hierarchy:
1. groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader$InnerLoader: groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader$InnerLoader@7e3f7bbe
2. groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader: groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader@3176bcb3
3. com.intellij.database.extensions.ExtensionScriptsUtil$1: com.intellij.database.extensions.ExtensionScriptsUtil$1@7accdcc1
4. com.intellij.ide.plugins.cl.PluginClassLoader: PluginClassLoader
(
plugin=PluginDescriptor
(
name=Database Tools and SQL,
id=com.intellij.database,
descriptorPath=plugin.xml,
path=~/Library/Application Support/JetBrains/Toolbox/apps/IDEA-U/ch-0/232.9921.47/IntelliJ IDEA.app/Contents/plugins/DatabaseTools,
version=232.9921.47,
package=null,
isBundled=true
),
packagePrefix=null,
state=active
)
The most intriguing entry here is the PluginClassLoader, which seems to load libraries from the
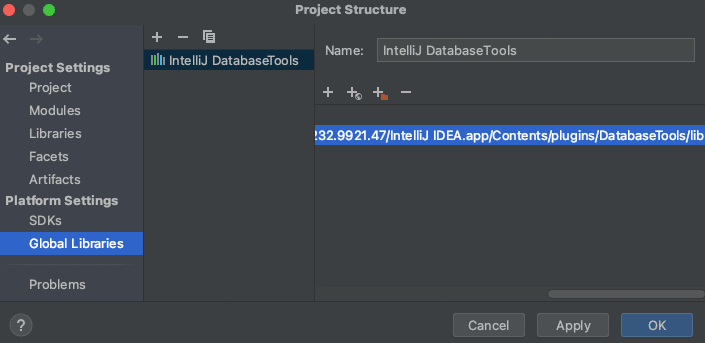
Contents/plugins/DatabaseTools path relative to the location of the installed IDE. By adding libraries from this
module to the IntelliJ project in the next step (File > Project Structure > Platform Settings > Global Libraries),
you can finally preview the (decompiled) code of the class used and deduce its functionality.
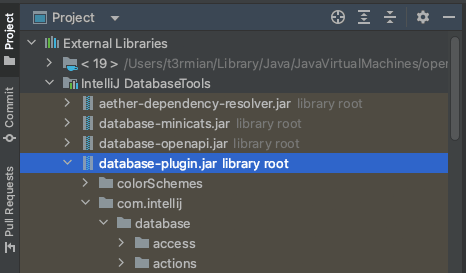
This way, you can also look at other utility classes in other packages, keeping in mind that they may
change with IDE updates. In the case of the mentioned areKeywordsLowerCase method, the code shows that it is an editor
preference for SQL in the Code Style section (General > Word Case > Keywords)
