How does Android Lint verify the use of SDK methods?
When starting the development of an Android application, the first thing that must be performed is the selection of
the supported Android API versions. Three parameters that are connected with this chore can be set in the build.gradle file:
compileSdkVersionthis is the SDK API version against which we will compile the application;targetSdkVersionis the maximum API version on which our application has been verified – lower than or equal to the version ofcompileSdkVersion;minSdkVersionis simply the lowest API version that contains all required methods for the application to work properly.
In order to test whether a given method can be used in the selected API range (from minSdkVersion to compileSdkVersion), Android Studio
performs a static analysis of our code. More specifically, it is the Lint tool ($ANDROID_HOME/tools/bin/lint[.bat]) and its NewApi check
defined in the com.android.tools.lint.checks.ApiDetector class. At the same time, we can invoke them through the Gradle wrapper
and its special task: ./gradlew: app:lint.
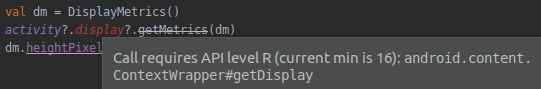
Android Lint NewApi
It is thanks to the NewApi check that we know, for example, that the Android API method we use,
is not available on the expected API versions. It forces us to come up with an alternative implementation for legacy devices.
For such a case, the tool understands the separation of parts of the code for specific API versions
through the comparison to the runtime API version in the Build.VERSION.SDK_INT property.
private fun getDisplayHeight() = if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.R) {
activity?.windowManager?.currentWindowMetrics?.bounds?.height() ?: 0
} else {
val dm = DisplayMetrics()
activity?.windowManager?.defaultDisplay?.getMetrics(dm)
dm.heightPixels
}
The methods used by your application are compared against the database consisting of methods, classes, and versions in which they were introduced.
For API SDK version less than 26 (Oreo), this database is being loaded from Platform-Tools $ANDROID_HOME/tools/api/api-versions.xml.
In the case of newer versions of the SDK (and lint-checks library), this database is already being initialized from the same file,
but from the platforms directory $ANDROID_HOME/platforms/android-*/data/api-versions.xml.
When for some reason this check does not work, and we did not disable it, it is worth clearing the cache in Android Studio. After the initialization from an XML file, the database is cached in a binary format. I the end, we should also install the available updates and reinstall the SDK if it still doesn't work.
Such a problem is quite rare, but can hit you when you least expect it, especially when you work alone on the app:
--------- beginning of crash
03-06 11:03:53.207 3588-3588/dev.termian.nutrieval E/AndroidRuntime: FATAL EXCEPTION: main
Process: dev.termian.nutrieval, PID: 3588
java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method getDisplay()Landroid/view/Display; in class Landroid/content/Context; or its super classes (declaration of 'android.content.Context' appears in /system/framework/framework.jar)
at dev.termian.nutrieval.ui.home.HomeFragment.c2()
at dev.termian.nutrieval.ui.home.HomeFragment.V1()
at dev.termian.nutrieval.ui.home.HomeFragment$i$d.run()
at android.os.Handler.handleCallback(Handler.java:739)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:95)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:135)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:5221)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:372)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:899)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:694)
