WebLogic Filtering Classloader tips
If you are looking for a way to make the WebLogic load specific version of dependencies bundled with your application, here are some tips to keep your sanity:
- WebLogic as an application server comes with a lot of libraries that you might also be using in your application (possibly different versions of those).
- WebLogic follows the standard parent delegation during class loading. The requested class is first looked up (preferred) by the system, then the parent and application class loader.
- Filtering Class Loader is a feature in the WebLogic that allows the deployer to influence this process and invert some parts of it. With this, you can achieve similar loading as in Tomcat.
You can use the filtering class loader when you deploy either a WAR application or an EAR application. Two different descriptors are used depending on the archive type:
- weblogic-application.xml (EAR);
- weblogic.xml (WAR).
EAR descriptor
For an EAR descriptor, you will find a matching XML schema definition based on the schema versions list.
Replace the xsi:schemaLocation mapping with a version matching your WLS. Now moving to the descriptor,
the important settings are the prefer-application-packages and prefer-application-resources.
The first one is used to configure classes that should be loaded from your application instead of the WLS modules. The second property can be used for non-class resources like service loader configuration files.
Below you can see how to override commons-io:commons-io package that is bundled with WLS 12.1.3 (wlserver/
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<weblogic-application
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/weblogic/weblogic-application"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.oracle.com/weblogic/weblogic-application http://xmlns.oracle.com/weblogic/weblogic-application/1.8/weblogic-application.xsd">
<prefer-application-packages>
<package-name>org.apache.commons.io.*</package-name>
</prefer-application-packages>
<prefer-application-resources>
<resource-name>META-INF/services/javax.ws.rs.ext.RuntimeDelegate</resource-name>
</prefer-application-resources>
</weblogic-application>
The correct location for this descriptor is EAR/META-INF/weblogic-application.xml. By default, if you put it in the src/main/application/META-INF/weblogic-application.xml,
maven-ear-plugin will be bundled into the said directory. Otherwise, the plugin earSourceDirectory configuration property defines the place where you should put the META-INF directory.
WAR descriptor
The schema location for the weblogic.xml is also specific to the WLS version.
Note that since WLS 12.1.3, there is also a version offset as compared to the EAR descriptor.
Although the schema is different, the configuration is similar to the above:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<weblogic-web-app
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/weblogic/weblogic-web-app"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.oracle.com/weblogic/weblogic-web-app http://xmlns.oracle.com/weblogic/weblogic-web-app/1.7/weblogic-web-app.xsd">
<container-descriptor>
<prefer-application-packages>
<package-name>org.apache.commons.io.*</package-name>
</prefer-application-packages>
<prefer-application-resources>
<resource-name>META-INF/services/javax.ws.rs.ext.RuntimeDelegate</resource-name>
</prefer-application-resources>
</container-descriptor>
</weblogic-web-app>
This time the descriptor should go to the WAR/WEB-INF/weblogic.xml. With the maven-war-plugin, it will be picked by default from the src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/weblogic.xml.
One additional configuration is possible with the WAR deployment. Suppose you have conflicting class versions between your package classes and dependencies. In a such case you can force the class loader to prefer your classes over the classes from dependencies or from the WLS:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<weblogic-web-app
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/weblogic/weblogic-web-app"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.oracle.com/weblogic/weblogic-web-app http://xmlns.oracle.com/weblogic/weblogic-web-app/1.7/weblogic-web-app.xsd">
<container-descriptor>
<prefer-web-inf-classes>true</prefer-web-inf-classes>
</container-descriptor>
</weblogic-web-app>
Combining this option with the prefer-application-packages/prefer-application-resources is not valid.
Troubleshooting
You may wonder whether the correct classes/resources are properly loaded during the runtime.
Often, a clear indication of conflict is java.lang.NoSuchMethodError exception.
It appears during the runtime, signaling that the loaded class is missing referenced method signature.
Other less common errors include:
java.lang.AbstractMethodError;java.lang.IllegalAccessError;java.lang.IncompatibleClassChangeError;java.lang.NoSuchFieldError;java.lang.NoSuchMethodError.
You can find a complete list of them in the tree of exceptions inheriting from java.lang.LinkageError.
Sometimes there is no clear error, but you might be unsure of the class sources. In such case you can quickly find out the source, e.g.:
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().loadClass("org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils").getProtectionDomain().getCodeSource().getLocation();Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource("META-INF/services/javax.ws.rs.ext.RuntimeDelegate").getPath());
Compatibility and conflicts
Most often, the WLS libraries will come from /oracle_common/modules directory, where you can verify the version based on the JAR name.
If there is no version suffix, you can open the archive and look for META-INF manifest or Maven metadata.
For finding out the source/binary compatibility, there is the JAPICC japi-compliance-checker – a popular tool that you can install with your system package manager
and get more insights about possible linking problems.
Otherwise, there is a WLS-specific tool called CAT (Classloader Analysis Tool).
As a web application, it is bundled with the fat WLS installation and, by default, deployed under the /wls-cat context.
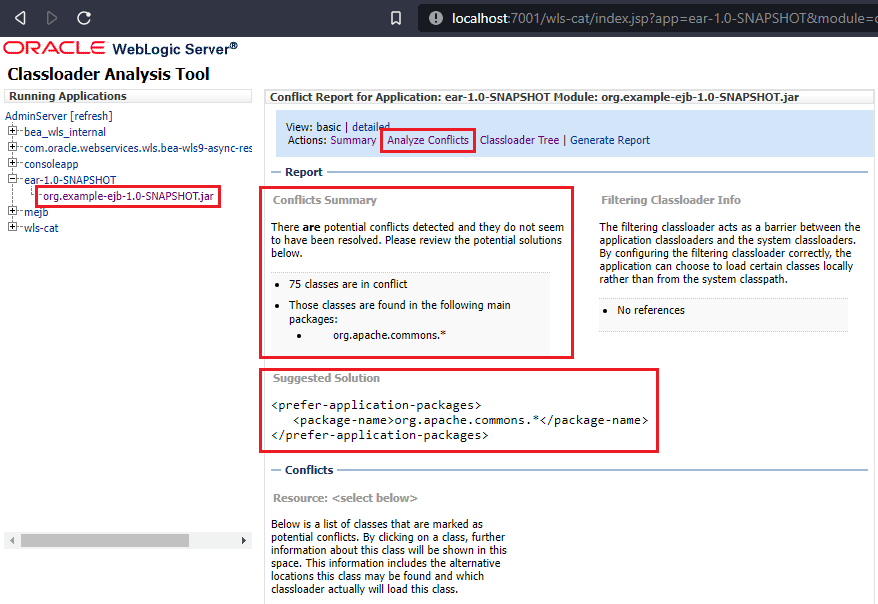
Select your application in the tree on the left and then go to the 'Analyze Conflicts' tab to verify potential packages that are in conflict, as well as the suggested solutions. After configuring the filtering, the list should be shorter. Hit refresh and go to the 'Classloader Tree' to verify the filtering. Conflicts in the direct EJB/WAR classes and dependencies should get detected properly.
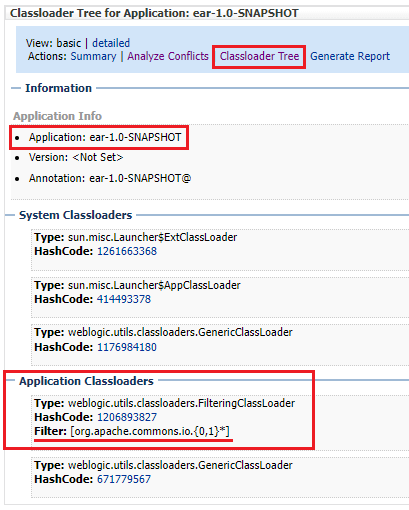
Even though there also seems to be a separate filtering class loader for the standalone EJB deployments, I did not
find a clean way to configure it. Neither the weblogic-application.xml nor weblogic.xml descriptors fit here, nor the '-ejb' one has such a configuration property.
Thus, I suggest simply wrapping the EJB module into an EAR in this case.
Java 9 support
Lastly, on old WLS versions, you may encounter the following error:
java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: module-info has been compiled by a more recent version of the Java Runtime (class file version 53.0), this version of the Java Runtime only recognizes class file versions up to 52.0
Some libraries have added support for Java 9 module encapsulation. Even though the library can be run on Java 8, it is accompanied by a module-info, usually either at the root of the library or at the META-INF/versions directory.
In the case of WLS, this can cause errors at the runtime as the file is compiled for Java 9:
- caused by default CDI scanning configurable by
beans.xml; - prevents CAT scanning.
The most straightforward approach is to remove it from the library, e.g. using the truezip-maven-plugin plugin during a relevant phase.
Take a look at the following configuration that removes incompatible files for log4j bundled within WAR running on Java 8 WLS:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>truezip-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>remove-log4j2-java9-meta</id>
<goals>
<goal>remove</goal>
</goals>
<phase>package</phase>
<configuration>
<filesets>
<fileset>
<directory>
${basedir}/target/${project.build.finalName}.war/WEB-INF/lib/log4j-api-${log4j.version}.jar
</directory>
<includes>
<include>META-INF/versions</include>
</includes>
</fileset>
<fileset>
<directory>
${basedir}/target/${project.build.finalName}.war/WEB-INF/lib/log4j-core-${log4j.version}.jar
</directory>
<includes>
<include>META-INF/versions</include>
</includes>
</fileset>
</filesets>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
If CAT does not show the location of the incompatible module-info in the stacktrace, just grep all jars for it in the exploded directory.
Even though the jars are binary files, you should generally get some valid matches, if not, use the standard jar Java tool: jar tf <JAR> | grep module-info.
